VIDEO
正規のオンライン小売業者:
紹介
前のレッスンでは、Raspberry PiのデータをIIC(I2Cとも呼ばれる)を介して出力し、1602 LCDに文字を表示する方法を学びました。今回のレッスンでは、レッスン11とレッスン13で学んだ知識を組み合わせます。ポテンショメータを使用して電圧を変更し、MCP3008を介してアナログ信号をデジタル信号に変換し、SPIを介してPiに送信します。その後、PiはI2Cを介して電圧データを送信し、1602 LCD画面にデータを表示します。
1 * Raspberry Pi
ソフトウェアの準備 lesson 1: getting started with raspberry pi をご覧ください。
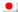
ポテンショメータの作業原理
ポテンショメータは、2つの端子とワイパーを持つ可変抵抗器であり、ワイパーをスライドして抵抗値を調整することで、端子の1つとワイパーを使用して可変抵抗器を作成することができます。詳細については、here をクリックしてください。
ポテンショメータの構造と動作は、以下の図から理解できます。AとBは端子で、Cはワイパーです。
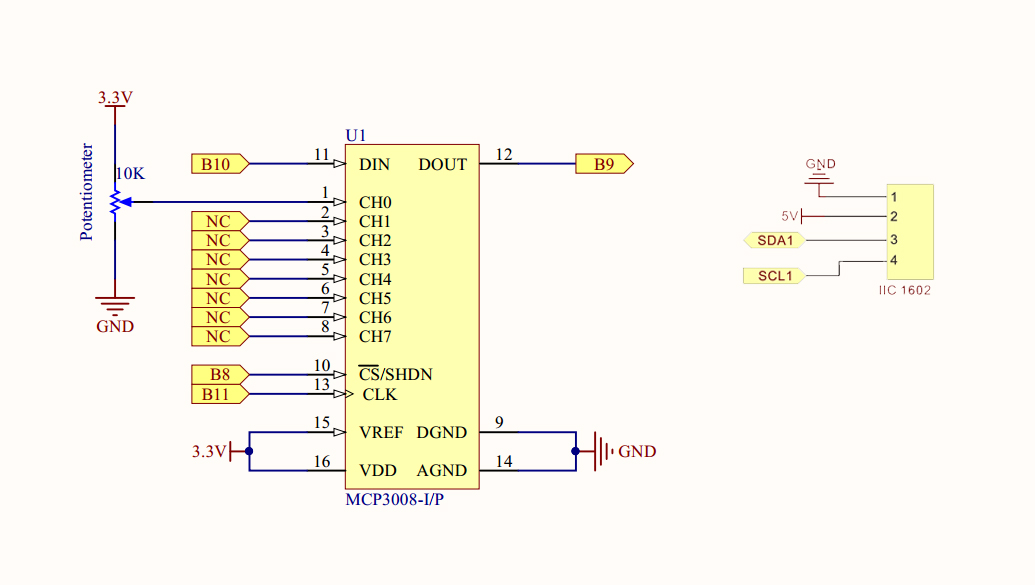
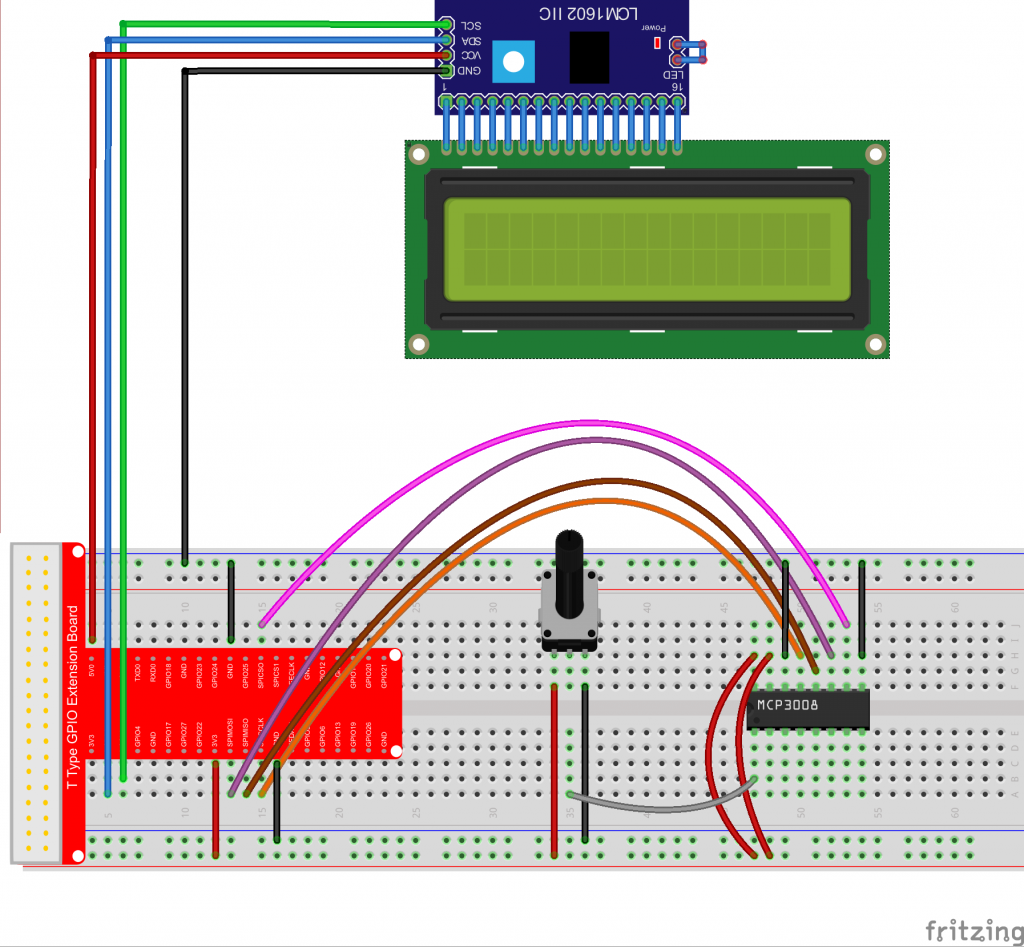
ハードウェアの設定
このプロジェクトでは、Piを外部のMCP3008 ADCに配線し、そこからアナログ値を測定します。その後、1602 LCDに電圧値を表示します。回路図は以下のようになります。
SPIとI2Cを有効にする方法については、lesson10 and lesson13 を読んでください。
C言語ユーザーの場合
cd ~
sudo wget http://osoyoo.com/driver/pi3_start_learning_kit_lesson_15/voltmeter.c
サンプルコードファイルをカスタマイズしたい場合は、次のコマンドを入力してnanoエディターを使用してソースコードを編集することができます:
sudo nano voltmeter.c
2)コードをコンパイルする
gcc -Wall -o voltmeter voltmeter.c -lwiringPi
3) プログラムを実行する
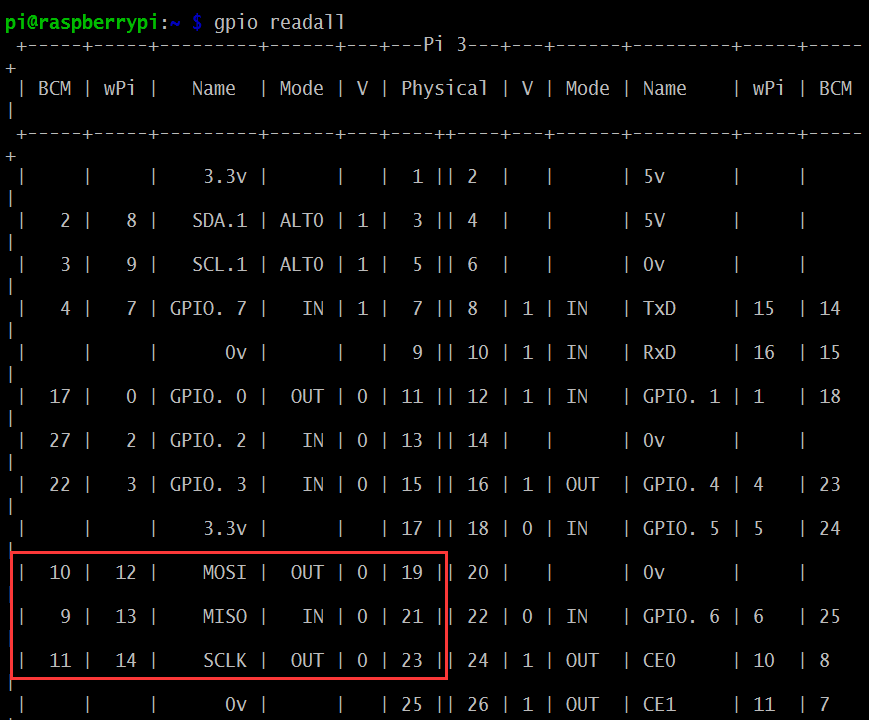
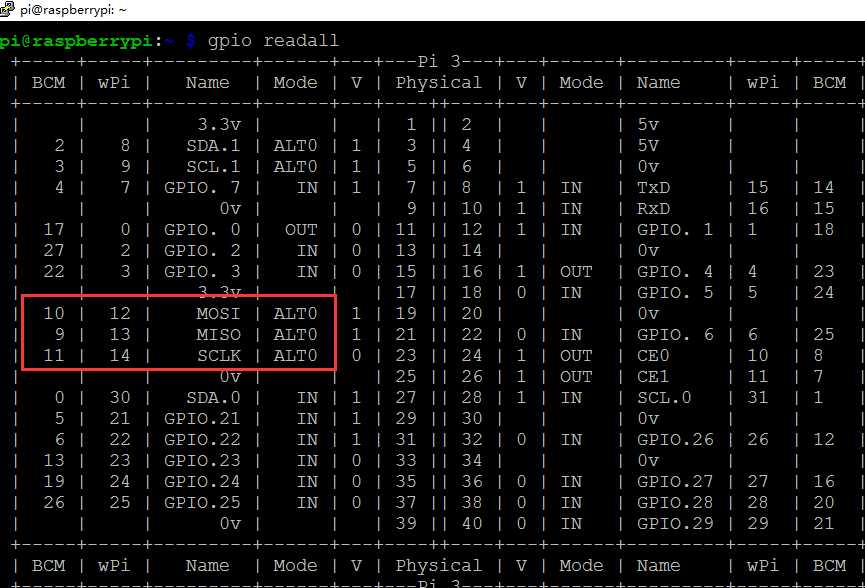
プログラムを実行する前に、コマンド gpio readall を実行して、MOSI、MISO、SCLK(B10、B9、B11) が代替機能として機能するかどうかを確認してください。ターミナルが次のように表示される場合:
代替機能として変更するには、次のコマンドを実行してください
gpio -g mode 9 alt0 gpio -g mode 10 alt0 gpio -g mode 11 alt0
ターミナルが次のように表示されたら、プログラムを実行してください。
sudo ./voltmeter
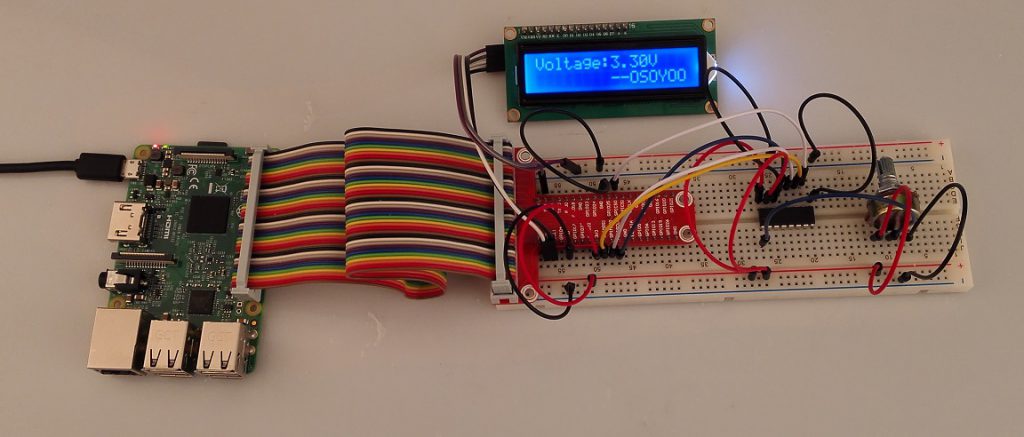
4) 実行結果
プログラムを実行すると、ターミナルにはまずコードの印刷メッセージが表示されます。1602 LCDには、ポテンショメータの電圧が表示され、ポテンショメータのシャフトを回して0〜3.3Vの間の電圧を調整します。
C 言語コードの解析
#include < stdint.h>
#include < string.h>
#include < errno.h>
#include < wiringPi.h>
#include < stdio.h>
#include < stdlib.h>
#include < wiringPiSPI.h>
#include < wiringPiI2C.h>
#define LCDADDR 0x3F //IIC LCD address
#define BLEN 1 //1--open backlight,0--close backlight
#define CHAN_CONFIG_SINGLE 8 //setup channel 0 as Single-ended input
#define SPICHANNEL 0 //MCP3008 connect to SPI0
#define ANALOGCHANNEL 0 //Potentiometer connect MCP3008 analog channel 0
static int spifd ;
static int i2cfd;
void spiSetup (int spiChannel)
{
if ((spifd = wiringPiSPISetup (spiChannel, 10000)) < 0)
{
fprintf (stderr, "Can't open the SPI bus: %s\n", strerror (errno)) ;
exit (EXIT_FAILURE) ;
}
}
int myAnalogRead(int spiChannel,int channelConfig,int analogChannel)
{
if(analogChannel7)
return -1;
unsigned char buffer[3] = {1}; // start bit
buffer[1] = (channelConfig+analogChannel) << 4;
wiringPiSPIDataRW(spiChannel, buffer, 3);
return ( (buffer[1] & 3 ) << 8 ) + buffer[2]; // get last 10 bits
}
void print_info()
{
printf("\n");
printf("|************************************|\n");
printf("| Voltemter |\n");
printf("| ------------------------- |\n");
printf("| | ADC | | Pi | |\n");
printf("| |-----|-----------|-----| |\n");
printf("| | CS | connect to| CE0 | |\n");
printf("| | Din | connect to| MOSI| |\n");
printf("| | Dout| connect to| MISO| |\n");
printf("| | CLK | connect to| SCLK| |\n");
printf("| | CH0 | connect to| 3.3V| |\n");
printf("| | CH1 | connect to| GND | |\n");
printf("|************************************|\n");
printf("| Potentiometer connect to ADC CH0 |\n");
printf("| OSOYOO|\n");
printf("|************************************|\n");
printf("\n");
}
//write a word to lcd
void write_word(int data){
int temp = data;
if ( BLEN == 1 )
temp |= 0x08;
else
temp &= 0xF7;
wiringPiI2CWrite(i2cfd, temp);
}
//send command to lcd
void send_command(int comm){
int buf;
// Send bit7-4 firstly
buf = comm & 0xF0;
buf |= 0x04; // RS = 0, RW = 0, EN = 1
write_word(buf);
delay(2);
buf &= 0xFB; // Make EN = 0
write_word(buf);
// Send bit3-0 secondly
buf = (comm & 0x0F) << 4;
buf |= 0x04; // RS = 0, RW = 0, EN = 1
write_word(buf);
delay(2);
buf &= 0xFB; // Make EN = 0
write_word(buf);
}
//send data to lcd
void send_data(int data){
int buf;
// Send bit7-4 firstly
buf = data & 0xF0;
buf |= 0x05; // RS = 1, RW = 0, EN = 1
write_word(buf);
delay(2);
buf &= 0xFB; // Make EN = 0
write_word(buf);
// Send bit3-0 secondly
buf = (data & 0x0F) << 4;
buf |= 0x05; // RS = 1, RW = 0, EN = 1
write_word(buf);
delay(2);
buf &= 0xFB; // Make EN = 0
write_word(buf);
}
//initialize the lcd
void init(){
send_command(0x33); // Must initialize to 8-line mode at first
delay(5);
send_command(0x32); // Then initialize to 4-line mode
delay(5);
send_command(0x28); // 2 Lines & 5*7 dots
delay(5);
send_command(0x0C); // Enable display without cursor
delay(5);
send_command(0x01); // Clear Screen
wiringPiI2CWrite(i2cfd, 0x08);
}
//clear screen
void clear(){
send_command(0x01); //clear Screen
}
//Print the message on the lcd
void write(int x, int y, char data[]){
int addr, i;
int tmp;
if (x < 0) x = 0; if (x > 15) x = 15;
if (y < 0) y = 0; if (y > 1) y = 1;
// Move cursor
addr = 0x80 + 0x40 * y + x;
send_command(addr);
tmp = strlen(data);
for (i = 0; i < tmp; i++){
send_data(data[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int adc;
float voltage;
char buf[5];
if(wiringPiSetup() < 0)
{ fprintf(stderr,"Can't init wiringPi: %s\n",strerror(errno));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
spiSetup(SPICHANNEL);//init spi
i2cfd = wiringPiI2CSetup(LCDADDR);//init i2c
init();//init LCD
clear();//clear screen
print_info();
while(1)
{
adc = myAnalogRead(SPICHANNEL,CHAN_CONFIG_SINGLE,ANALOGCHANNEL);
voltage = adc/1024.*3.3;
write(0,0,"Voltage:");
sprintf(buf,"%1.2f",voltage);//float change to string
write(8,0,buf);//print voltage on lcd
write(12,0,"V");//print unit
write(8,1,"--OSOYOO");
delay(1000);
}
return 0;
}
1) 次のコマンドを入力してPythonのサンプルコードをダウンロードします。
cd ~
sudo wget http://osoyoo.com/driver/pi3_start_learning_kit_lesson_15/voltmeter.py
サンプルコードファイルをカスタマイズしたい場合は、次のコマンドを入力してnanoエディターを使用してソースコードを編集することができます:
2) プログラムを実行する
sudo python ./voltmeter.py
3) 実行結果
プログラムを実行すると、ターミナルにはまずコードの印刷メッセージが表示されます。1602 LCDには、ポテンショメータの電圧が表示され、ポテンショメータのシャフトを回して0〜3.3Vの間の電圧を調整します。
Pythonのサンプルコードの解析
import time
import os
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import smbus
# Define some device parameters
I2C_ADDR = 0x3F # I2C device address, if any error, change this address to 0x27
LCD_WIDTH = 16 # Maximum characters per line
# Define some device constants
LCD_CHR = 1 # Mode - Sending data
LCD_CMD = 0 # Mode - Sending command
LCD_LINE_1 = 0x80 # LCD RAM address for the 1st line
LCD_LINE_2 = 0xC0 # LCD RAM address for the 2nd line
LCD_LINE_3 = 0x94 # LCD RAM address for the 3rd line
LCD_LINE_4 = 0xD4 # LCD RAM address for the 4th line
LCD_BACKLIGHT = 0x08 # On
#LCD_BACKLIGHT = 0x00 # Off
ENABLE = 0b00000100 # Enable bit
# Timing constants
E_PULSE = 0.0005
E_DELAY = 0.0005
# change these as desired - they're the pins connected from the
# SPI port on the ADC to the Cobbler
SPICLK = 11
SPIMISO = 9
SPIMOSI = 10
SPICS = 8
analogChannel = 0
#Open I2C interface
#bus = smbus.SMBus(0) # Rev 1 Pi uses 0
bus = smbus.SMBus(1) # Rev 2 Pi uses 1
#setup function for some setup---custom function
def setup():
#set the gpio modes to BCM numbering
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# set up the SPI interface pins
GPIO.setup(SPIMOSI, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(SPIMISO, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(SPICLK, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(SPICS, GPIO.OUT)
pass
def lcd_init():
# Initialise display
lcd_byte(0x33,LCD_CMD) # 110011 Initialise
lcd_byte(0x32,LCD_CMD) # 110010 Initialise
lcd_byte(0x06,LCD_CMD) # 000110 Cursor move direction
lcd_byte(0x0C,LCD_CMD) # 001100 Display On,Cursor Off, Blink Off
lcd_byte(0x28,LCD_CMD) # 101000 Data length, number of lines, font size
lcd_byte(0x01,LCD_CMD) # 000001 Clear display
time.sleep(E_DELAY)
def lcd_byte(bits, mode):
# Send byte to data pins
# bits = the data
# mode = 1 for data
# 0 for command
bits_high = mode | (bits & 0xF0) | LCD_BACKLIGHT
bits_low = mode | ((bits<<4) & 0xF0) | LCD_BACKLIGHT # High bits bus.write_byte(I2C_ADDR, bits_high) lcd_toggle_enable(bits_high) # Low bits bus.write_byte(I2C_ADDR, bits_low) lcd_toggle_enable(bits_low) def lcd_toggle_enable(bits): # Toggle enable time.sleep(E_DELAY) bus.write_byte(I2C_ADDR, (bits | ENABLE)) time.sleep(E_PULSE) bus.write_byte(I2C_ADDR,(bits & ~ENABLE)) time.sleep(E_DELAY) def lcd_string(message,line): # Send string to display message = message.ljust(LCD_WIDTH," ") lcd_byte(line, LCD_CMD) for i in range(LCD_WIDTH): lcd_byte(ord(message[i]),LCD_CHR) #print message at the begining ---custom function def print_message(): print ('|**********************************|') print ('| Voltmeter |') print ('| ------------------------- |') print ('| | ADC | | Pi | |') print ('| |-----|-----------|-----| |') print ('| | CS | connect to| CE0 | |') print ('| | Din | connect to| MOSI| |') print ('| | Dout| connect to| MISO| |') print ('| | CLK | connect to| SCLK| |') print ('| | CH0 | connect to| 3.3V| |') print ('| | CH1 | connect to| GND | |') print ('| ------------------------- |') print ('| Potentiometer connect to CH0 |') print ('| OSOYOO|') print ('|**********************************|\n') print ('Program is running...') print ('Please press Ctrl+C to end the program...') # read SPI data from MCP3008 chip, 8 possible adc's (0 thru 7) def readadc(adcnum, clockpin, mosipin, misopin, cspin): if ((adcnum > 7) or (adcnum < 0)):
return -1
GPIO.output(cspin, True)
GPIO.output(clockpin, False) # start clock low
GPIO.output(cspin, False) # bring CS low
commandout = adcnum
commandout |= 0x18 # start bit + single-ended bit
commandout <<= 3 # we only need to send 5 bits here
for i in range(5):
if (commandout & 0x80):
GPIO.output(mosipin, True)
else:
GPIO.output(mosipin, False)
commandout <<= 1
GPIO.output(clockpin, True)
GPIO.output(clockpin, False)
adcout = 0
# read in one empty bit, one null bit and 10 ADC bits
for i in range(12):
GPIO.output(clockpin, True)
GPIO.output(clockpin, False)
adcout <<= 1 if (GPIO.input(misopin)): adcout |= 0x1 GPIO.output(cspin, True) adcout >>= 1 # first bit is 'null' so drop it
return adcout
#main function
def main():
#print info
print_message()
# Initialise display
lcd_init()
#clear screen
lcd_byte(0x01, LCD_CMD)
while True:
adc = readadc(analogChannel, SPICLK, SPIMOSI, SPIMISO, SPICS)
voltage = round((adc/1024.*3.3),2)
voltage = str(voltage) #float change to string
lcd_string("Voltage: <",LCD_LINE_1)
lcd_string(voltage,LCD_LINE_2)
time.sleep(1.5)
#define a destroy function for clean up everything after the script finished
def destroy():
#release resource
GPIO.cleanup()
#
# if run this script directly ,do:
if __name__ == '__main__':
setup()
try:
main()
#when 'Ctrl+C' is pressed,child program destroy() will be executed.
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
pass
#clear screen
finally:
lcd_byte(0x01, LCD_CMD)













Where is the function to toggle the backlight on/off?
You can turn around the Potentiometer at the back of LCD to adjust LCD backlight
I know about the potentiometer. But i am asking about the function to turn off the backlight from the python code. the backlight consumes too much battery so i need to put it to sleep for some time.