VIDEO
正規のオンライン小売業者:
紹介
このレッスンでは、Raspberry Piを使用してDHT11温湿度センサーモジュールからデータを取得する方法を紹介します。
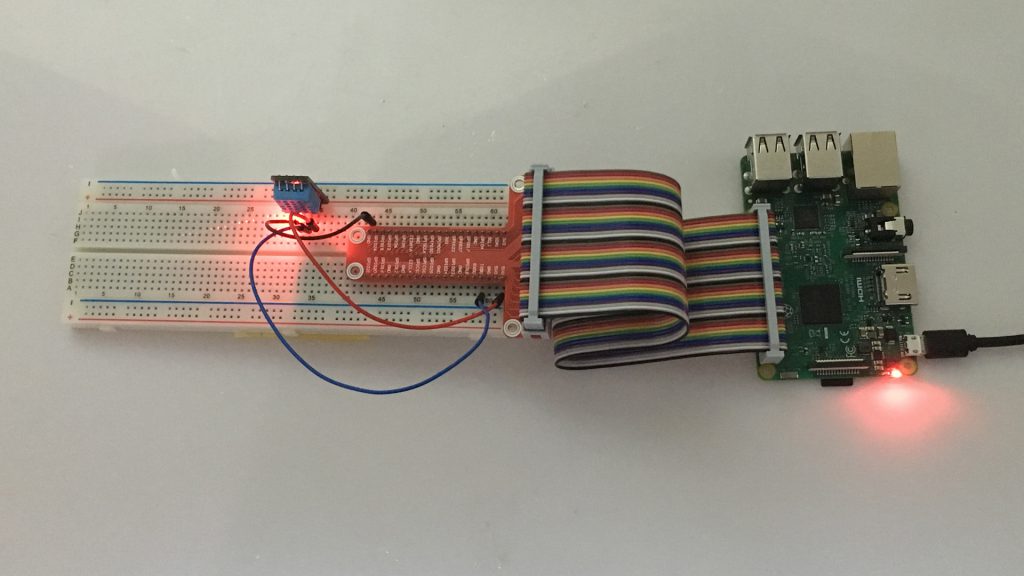
ハードウェアの準備
ソフトウェアの準備
実験原理
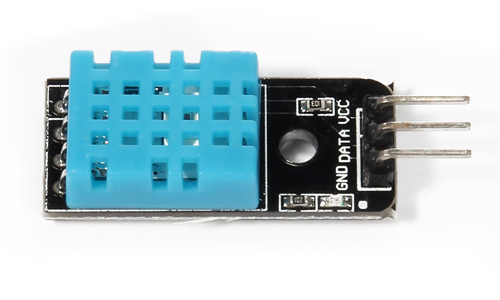
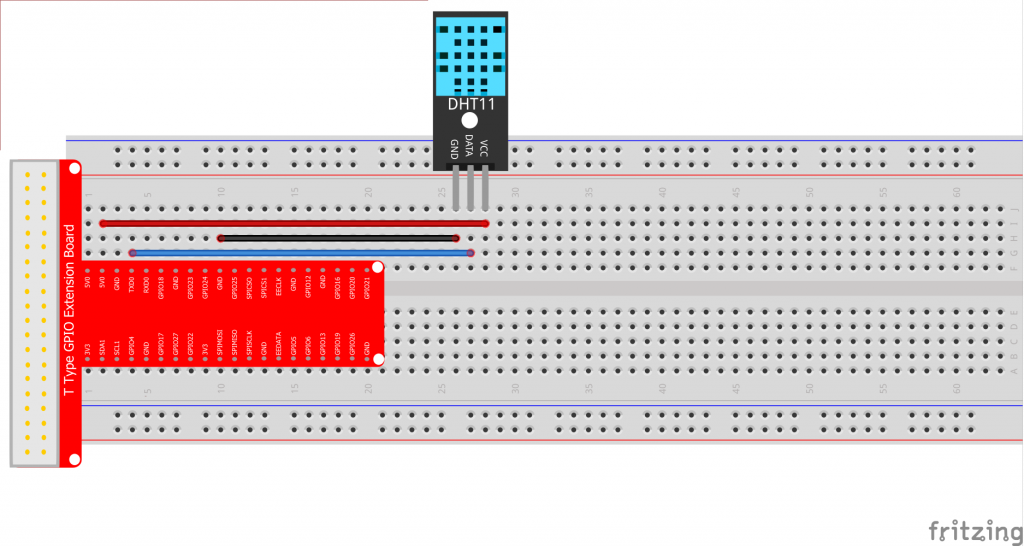
DHT11の回路図
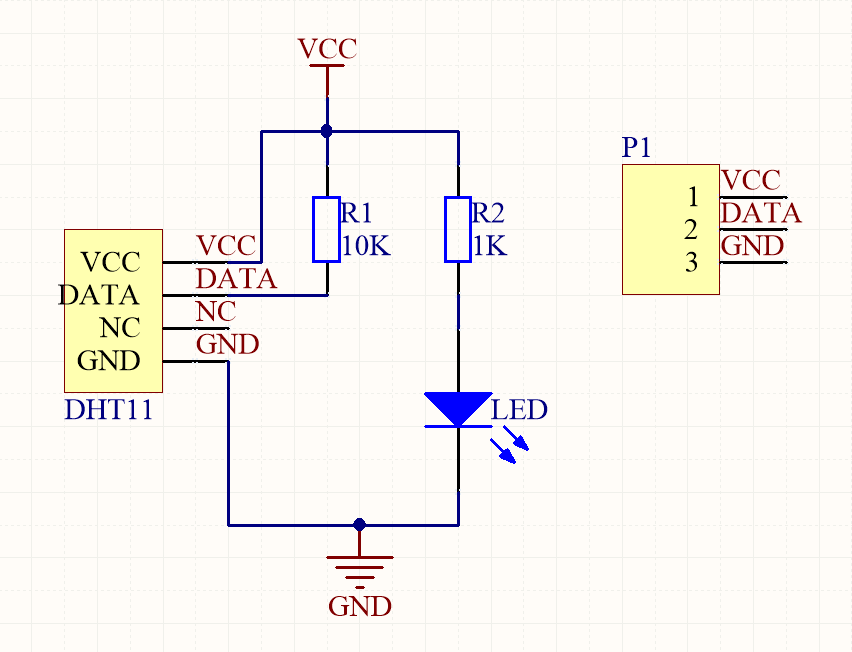
Raspberry PiとのDHT11の回路図
上記のグラフのB14はBCM GPIO#14(TXD)またはPhysical pin#8またはwiringPi#15を表します。 注:BはBCM(Broadcomピン番号)を意味します。BCMピン番号、Physical pin番号、wiringPi番号とは何かわからない場合は、レッスン3:Raspberry Pi GPIOの概要 をご覧ください。Raspberry PiのGPIOについて詳しく学ぶには、レッスン2:Raspberry Pi GPIOの概要 をご覧ください。
接続グラフ
ソフトウェア
C言語ユーザーとPython言語ユーザー向けに2種類のコードを提供します。
注意:wiringpiライブラリをインストールしていることを確認してください。here をクリックすると、wiringpiのインストールについて詳しく学べます。
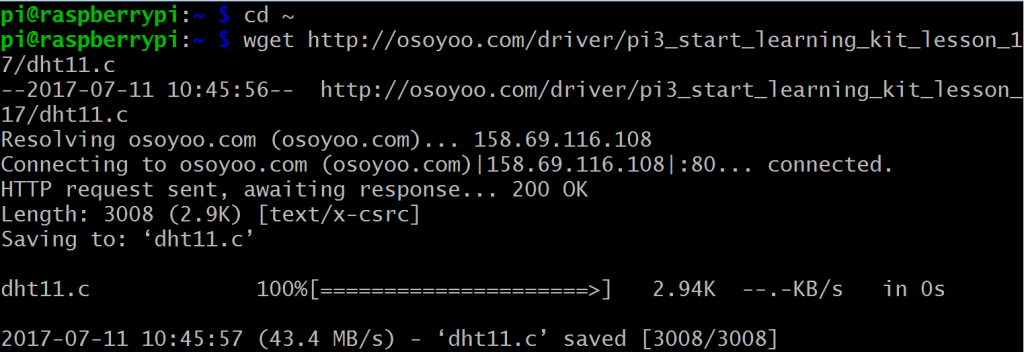
ステップ1) ターミナルに以下のコマンドを入力して、osoyoo.comからサンプルコードdht11.cをダウンロードしてください。
cd ~
wget http://osoyoo.com/driver/pi3_start_learning_kit_lesson_17/dht11.c
注:sudo nano dht11.c
3) コードをコンパイルする
gcc -Wall -o dht11 dht11.c -lwiringPi
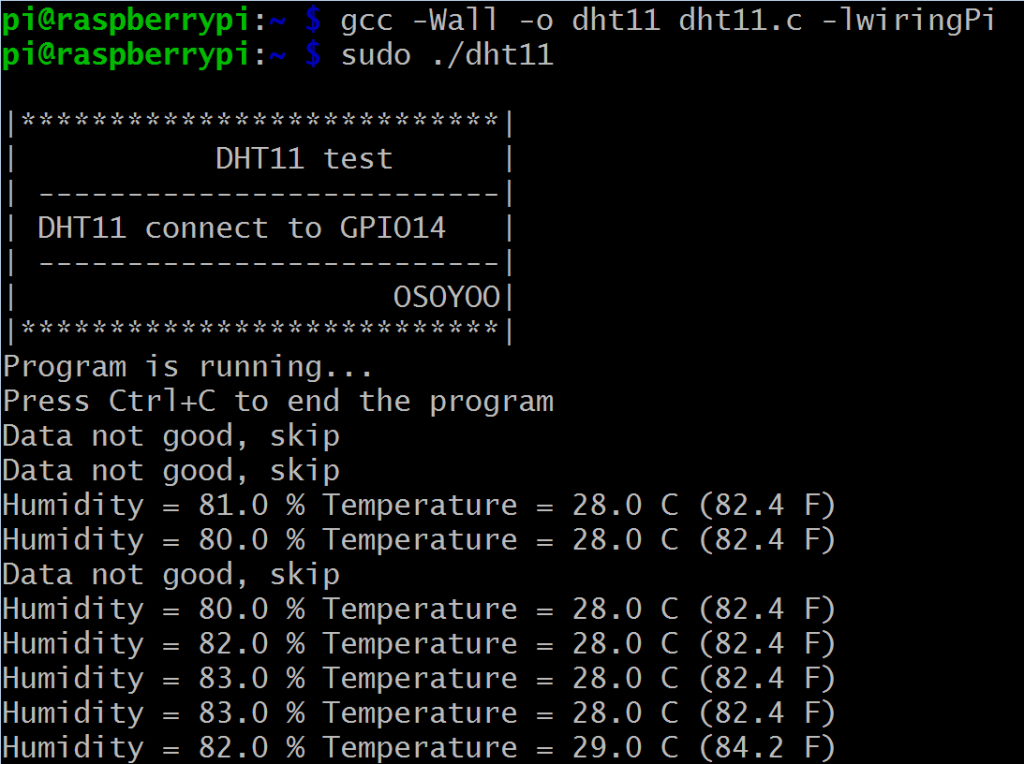
4) プログラムを実行する
sudo ./dht11
5) プログラムの結果
プログラムが実行されると、ターミナルに実際の温度と湿度が繰り返し表示されます。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define MAXTIMINGS 85
#define DHTPIN 15 //DHT connect to TxD
int dht11_dat[5] ={0,0,0,0,0};//store DHT11 data
void read_dht11_dat()
{
uint8_t laststate = HIGH;
uint8_t counter = 0;
uint8_t j = 0,i;
float f;//fahrenheit
dht11_dat[0] = dht11_dat[1] = dht11_dat[2] = dht11_dat[3] = dht11_dat[4] = 0;
//pull pin down to send start signal
pinMode( DHTPIN, OUTPUT );
digitalWrite( DHTPIN, LOW );
delay( 18 );
//pull pin up and wait for sensor response
digitalWrite( DHTPIN, HIGH );
delayMicroseconds( 40 );
//prepare to read the pin
pinMode( DHTPIN, INPUT );
//detect change and read data
for ( i = 0; i < MAXTIMINGS; i++ ) { counter = 0; while ( digitalRead( DHTPIN ) == laststate ) { counter++; delayMicroseconds( 1 ); if ( counter == 255 ) { break; } } laststate = digitalRead( DHTPIN ); if ( counter == 255 ) break; //ignore first 3 transitions if ( (i >= 4) && (i % 2 == 0) )
{
//shove each bit into the storage bytes
dht11_dat[j / 8] <<= 1; if ( counter > 16 )
dht11_dat[j / 8] |= 1;
j++;
}
}
//check we read 40 bits(8bit x 5) +verify checksum in the last byte
//print it out if data is good
if ( (j >= 40) &&
(dht11_dat[4] == ( (dht11_dat[0] + dht11_dat[1] + dht11_dat[2] + dht11_dat[3]) & 0xFF) ) )
{
f = dht11_dat[2] * 9. / 5. + 32;
printf( "Humidity = %d.%d %% Temperature = %d.%d C (%.1f F)\n",
dht11_dat[0], dht11_dat[1], dht11_dat[2], dht11_dat[3], f );
}
else
{
printf( "Data not good, skip\n" );
}
}
void print_info()
{
printf("\n");
printf("|***************************|\n");
printf("| DHT11 test |\n");
printf("| --------------------------|\n");
printf("| DHT11 connect to GPIO14 |\n");
printf("| --------------------------|\n");
printf("| OSOYOO|\n");
printf("|***************************|\n");
printf("Program is running...\n");
printf("Press Ctrl+C to end the program\n");
}
int main( void )
{
if ( wiringPiSetup() == -1 )
{
fprintf(stderr,"Can't init wiringPi: %s\n",strerror(errno));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
print_info();
while ( 1 )
{
read_dht11_dat();
delay(1000);//wait ls to refresh
}
return(0);
}
Pythonユーザー向け
Python言語でプログラミングする場合、通常、Rasbian Jessie OSに付属するGPIOライブラリであるRPi.GPIOを使用します。こちら をクリックすると、RPI.GPIOとPythonについて詳しく学べます。
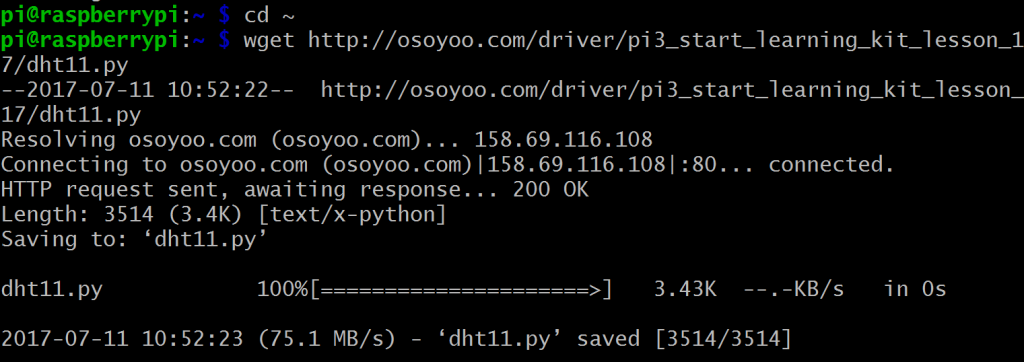
1) ターミナルコマンドに従って、サンプルのPythonコードを/home/piにダウンロードしてください。
cd ~
wget http://osoyoo.com/driver/pi3_start_learning_kit_lesson_17/dht11.py
注:
sudo nano dht11.py
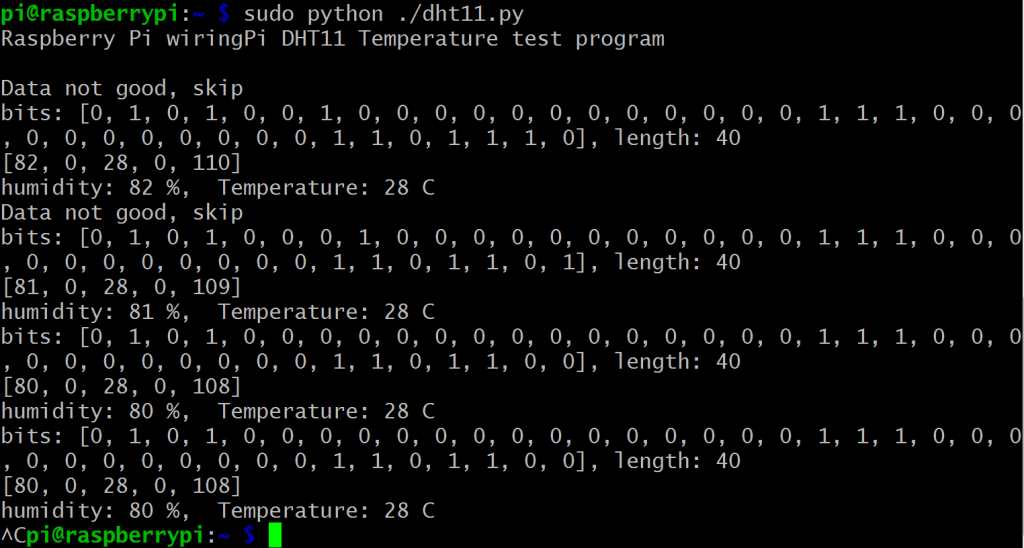
3) プログラムを実行する
sudo python ./dht11.py
4) プログラムの結果
プログラムが実行されると、ターミナルに実際の温度と湿度が繰り返し表示されます。
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
#DHT11 connect to BCM_GPIO14
DHTPIN = 14
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
MAX_UNCHANGE_COUNT = 100
STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN = 1
STATE_INIT_PULL_UP = 2
STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN = 3
STATE_DATA_PULL_UP = 4
STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN = 5
def read_dht11_dat():
GPIO.setup(DHTPIN, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(DHTPIN, GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.05)
GPIO.output(DHTPIN, GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(0.02)
GPIO.setup(DHTPIN, GPIO.IN, GPIO.PUD_UP)
unchanged_count = 0
last = -1
data = []
while True:
current = GPIO.input(DHTPIN)
data.append(current)
if last != current:
unchanged_count = 0
last = current
else:
unchanged_count += 1
if unchanged_count > MAX_UNCHANGE_COUNT:
break
state = STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN
lengths = []
current_length = 0
for current in data:
current_length += 1
if state == STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN:
if current == GPIO.LOW:
state = STATE_INIT_PULL_UP
else:
continue
if state == STATE_INIT_PULL_UP:
if current == GPIO.HIGH:
state = STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN:
if current == GPIO.LOW:
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_UP
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_PULL_UP:
if current == GPIO.HIGH:
current_length = 0
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN:
if current == GPIO.LOW:
lengths.append(current_length)
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_UP
else:
continue
if len(lengths) != 40:
print "Data not good, skip"
return False
shortest_pull_up = min(lengths)
longest_pull_up = max(lengths)
halfway = (longest_pull_up + shortest_pull_up) / 2
bits = []
the_bytes = []
byte = 0
for length in lengths:
bit = 0
if length > halfway:
bit = 1
bits.append(bit)
print "bits: %s, length: %d" % (bits, len(bits))
for i in range(0, len(bits)):
byte = byte << 1 if (bits[i]): byte = byte | 1 else: byte = byte | 0 if ((i + 1) % 8 == 0): the_bytes.append(byte) byte = 0 print the_bytes checksum = (the_bytes[0] + the_bytes[1] + the_bytes[2] + the_bytes[3]) & 0xFF if the_bytes[4] != checksum: print "Data not good, skip" return False return the_bytes[0], the_bytes[2] def main(): print "Raspberry Pi wiringPi DHT11 Temperature test program\n" while True: result = read_dht11_dat() if result: humidity, temperature = result print "humidity: %s %%, Temperature: %s C" % (humidity, temperature) time.sleep(1) def destroy(): GPIO.cleanup() if __name__ == '__main__': try: main() except KeyboardInterrupt: destroy()














Any suggestions on how to make this sensor on Scratch on Raspberry Pi? Scratch documentation only covers the DS18B20 sensor.
https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/usage/scratch/gpio/
Do you mean you want know how to connect the DHT11 sensor to Raspberry pi? or how to connect DS18B20 sensor to raspberry Pi?
Do you use raspberry Pi 2 or Pi 3?
If you want to learn more about GPIO port with raspberry Pi 3 and T type adapter, Please review our lessone 2: https://osoyoo.com/2017/06/26/introduction-of-raspberry-pi-gpio/.
Use DHT11 sensor with Raspberry pi.
I would like to code in Scratch, not Python or C, since I am using it to teach kids coding. The link I sent before https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/usage/scratch/gpio/ is general documentation for using Scratch to code on Pi, but it doesn’t cover your sensor DHT11. I am wondering if you have/could create some sample codes for Scratch.
It is Pi 3.
Thanks.