| Buy from US |
Buy from UK |
Buy from DE |
Buy from IT |
Buy from FR |
Buy from ES |
Buy from JP |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

In this lesson, we will learn how to programming RGB module and make the LED change color.


The reason that you can mix any color you like by varying the quantities of red, green and blue light is that your eye has three types of light receptor in it (red, green and blue). Your eye and brain process the amounts of red, green and blue and convert it into a color of the spectrum.
In a way, by using the three LEDs we are playing a trick on the eye. This same idea is used in TVs, where the LCD has red, green and blue color dots next to each other making up each pixel.
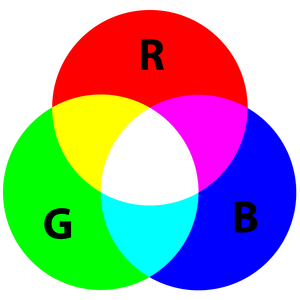
You can create one of those three colors – red, green or blue – by activating just one LED.
For example, if you want to produce blue, you activate the blue LED and turn off the other two.
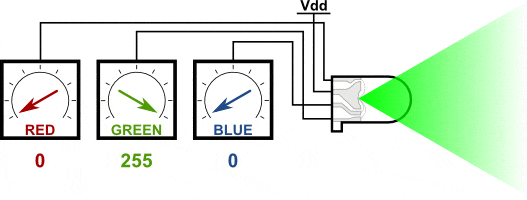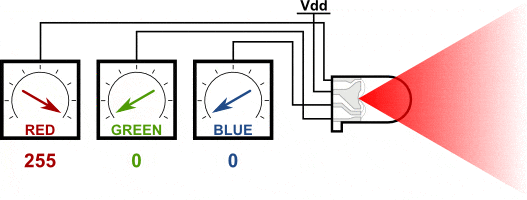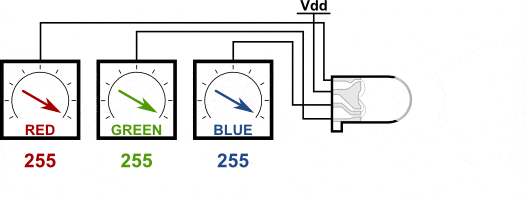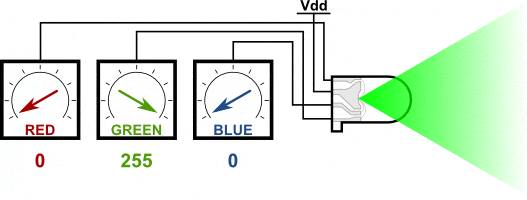
If we set the brightness of all three LEDs to be the same, then the overall color of the light will be white. If we turn off the blue LED, so that just the red and green LEDs are the same brightness, then the light will appear yellow.
We can control the brightness of each of the red, green and blue parts of the LED separately, making it possible to mix any color we like.
Black is not so much a color as an absense of light. So the closest we can come to black with our LED is to turn off all three colors.
PULSE-WIDTH MODULATION(PWM)
The brightness of an LED is proportional to the current going through it, but it would be rather difficult to use a microcontroller to accurately control the current flowing through an LED. Fortunately, human vision has a nice phenomenon called persistence of vision. Persistence of vision is the phenomenon where an image that is seen for only a fraction of a second will continue to be “seen” by your brain even after the original image has vanished or moved. This this the same principle behind film and television, where a rapidly changing image tricks your brain into seeing continuous motion. By turning our LED on and off rapidly, we can trick the brain into seeing an “average” value of brightness based on the duty cycle of the driving PWM signal.
Pulse-width modulation (PWM) is the practice of modulating the duty cycle of a signal, used in this application to control the average power sent to each LED. In the following figure, we show three different duty cycles, first with 50% duty cycle, then 10% and 90% duty cycle. During the 10% duty cycle, the signal is at the logic high level for only a brief time each cycle, but with 90% duty cycle, most of the signal’s period is spent at logic high level. If the frequency of the signal is fast enough, then there will be no visible flicker, and the LED’s brightness will be proportional to the signal’s duty cycle.
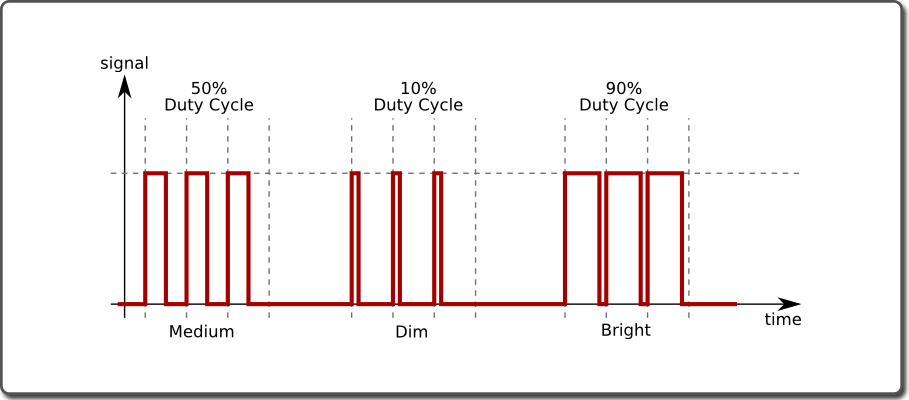
RGB LED COLOR CONTROL
RGB stands for the red, green, and blue color channels and is an industry color standard. RGB displays various new colors by changing the three channels and superimposing them, which, according to statistics, can create 16,777,216 different colors. If you say the color displayed doesn’t completely match a natural color, then it almost certainly cannot be differentiated with the naked eyes.
Each of the three color channels of red, green, and blue has 255 stages of brightness. When the three primary colors are all 0, “LED light” is the darkest, that is, it turns off. When the three primary colors are all 255, “LED light” is the brightest. When superimposing the light emitted by the three primary colors, the colors will be mixed. However, the brightness is equal to the sum of all brightness, and the more you mix, the brighter the LED is. This process is known as additive mixing

- Osoyoo UNO Board (Fully compatible with Arduino UNO rev.3) x 1
- OSOYOO Magic I/O Shield for Arduino x1
- RGB Module x 1
- OSOYOO 4-Pin PNP Cable x 1
- USB Cable x 1
- PC x 1

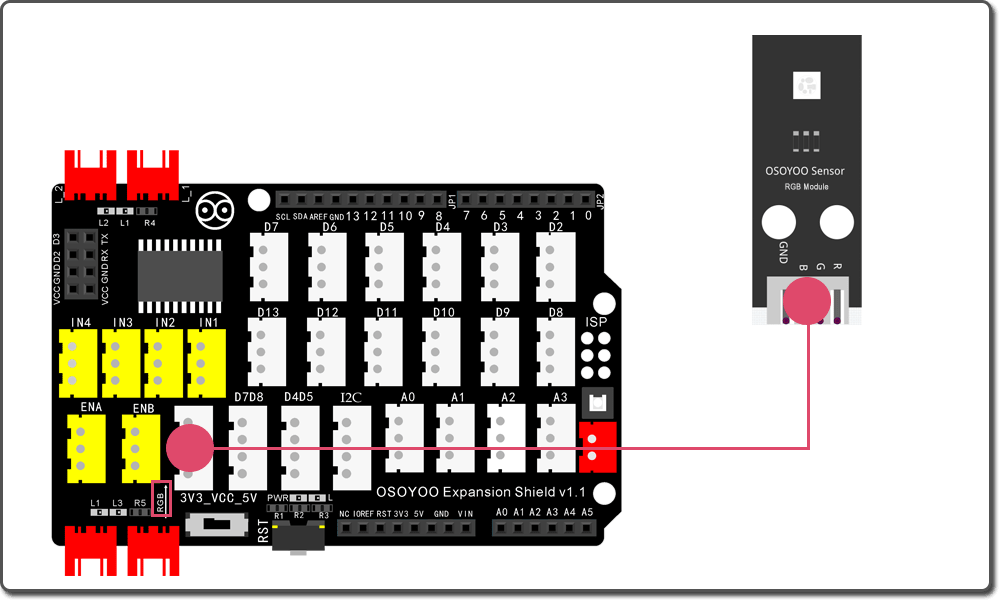
Firstly, please plug Osoyoo Magic I/O shield into UNO board as following:
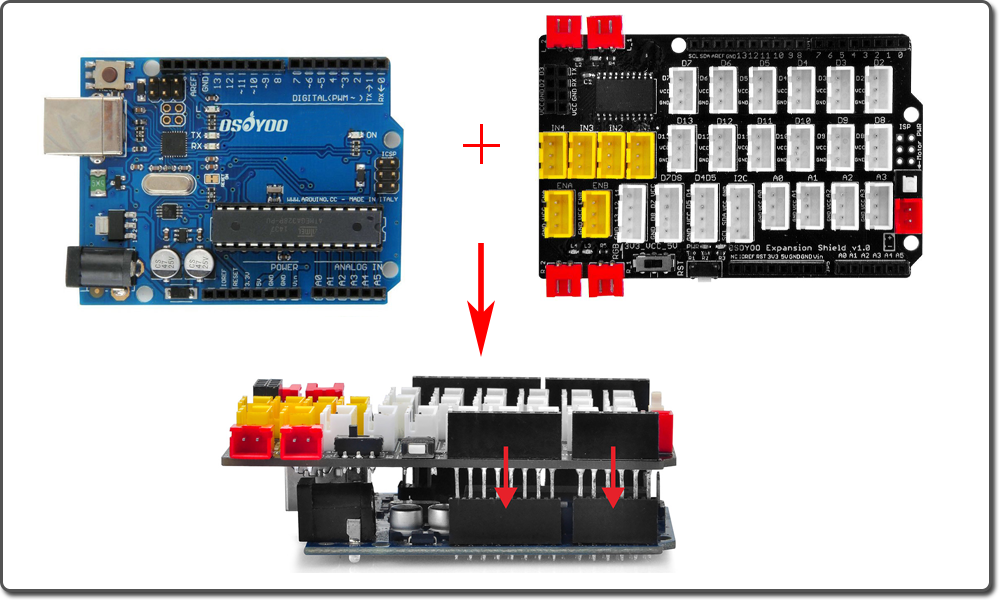
Then connect the RGB module to the RGB port of the Magic I/O shield with a 4-pin PNP cable as below:

Step 1) If you haven’t install mBlock software in your PC, please read Lesson 1, download and install the software.
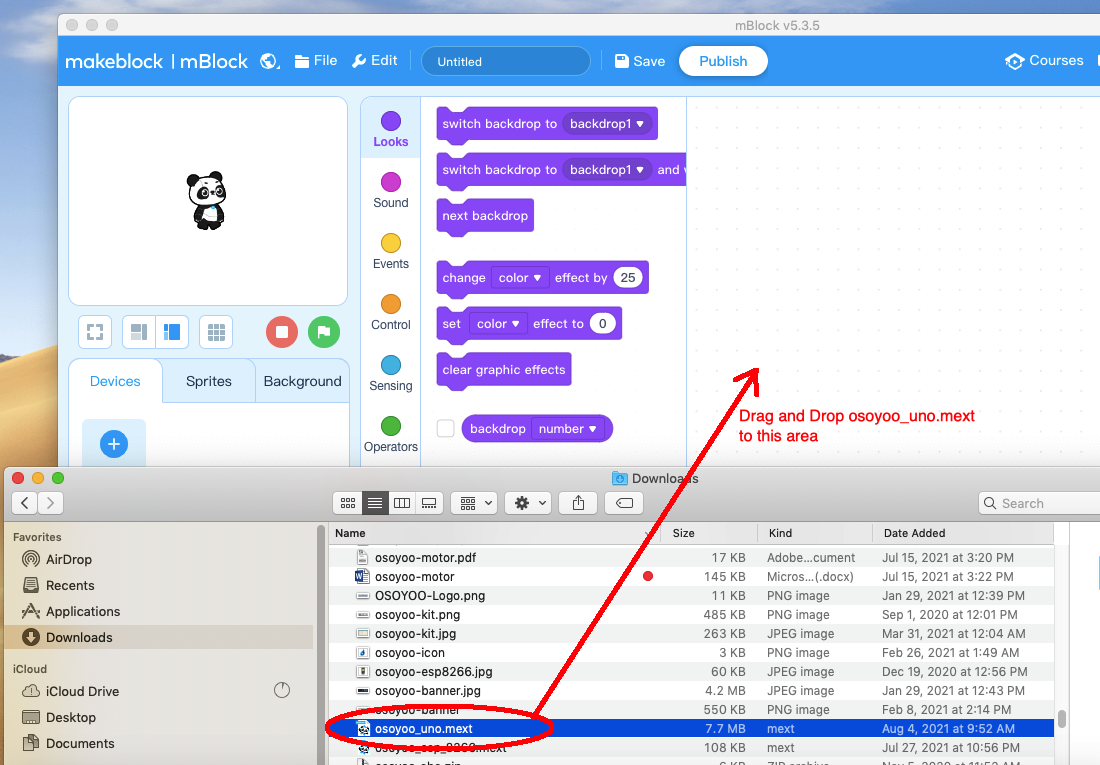
Step 2) Run the mBlock PC software by double click the lovely Panda icon. Drag and Drop osoyoo_uno_mext file(downloaded in Step 1) to mBlock software as following:
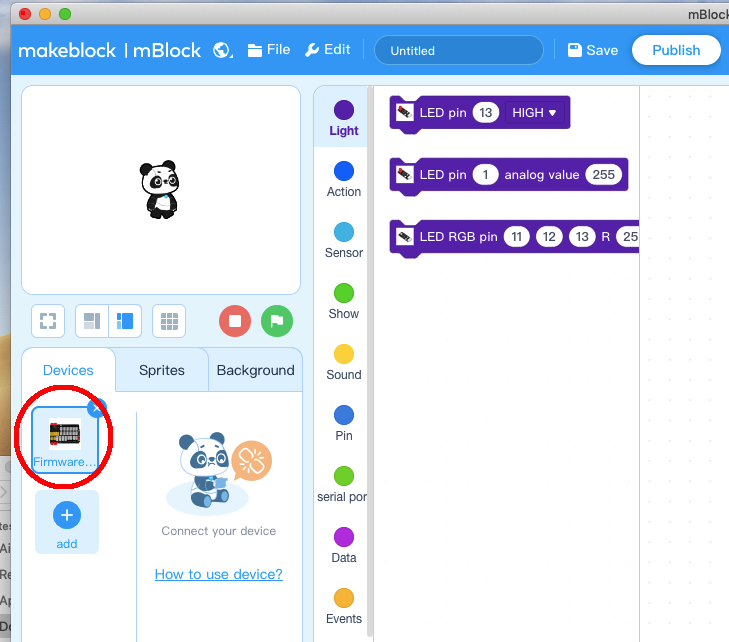
Now you will see a new device firmware in mBlock, see following picture:
Now mBlock software and OSOYOO_UNO device firmware have been successfully installed in our PC!
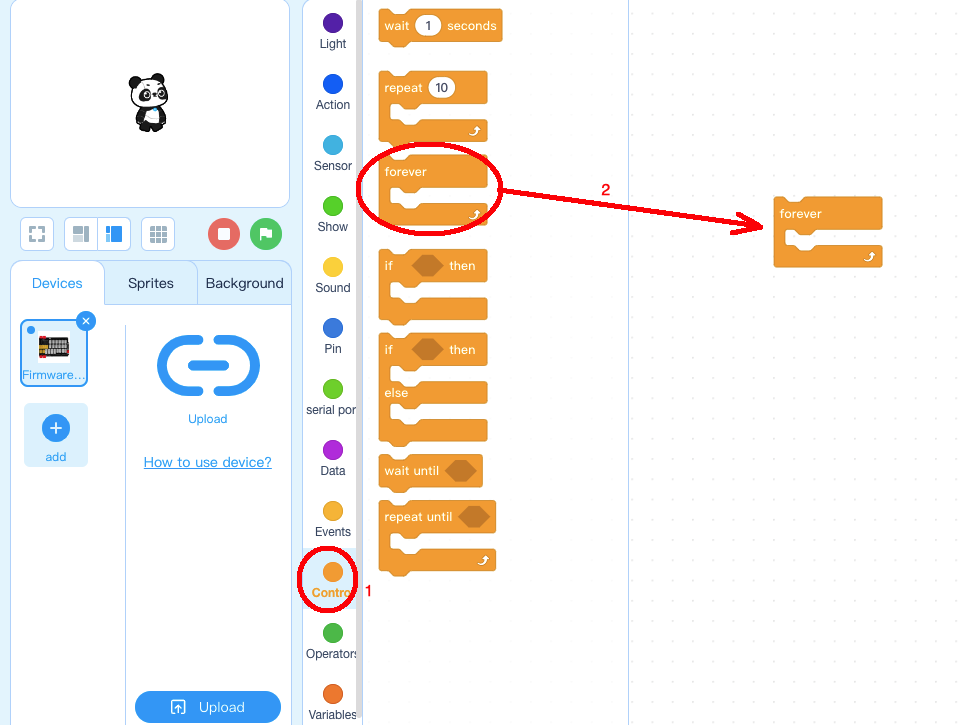
Step 1: Click Control, then Drag and drop Forever block to programming area as following:
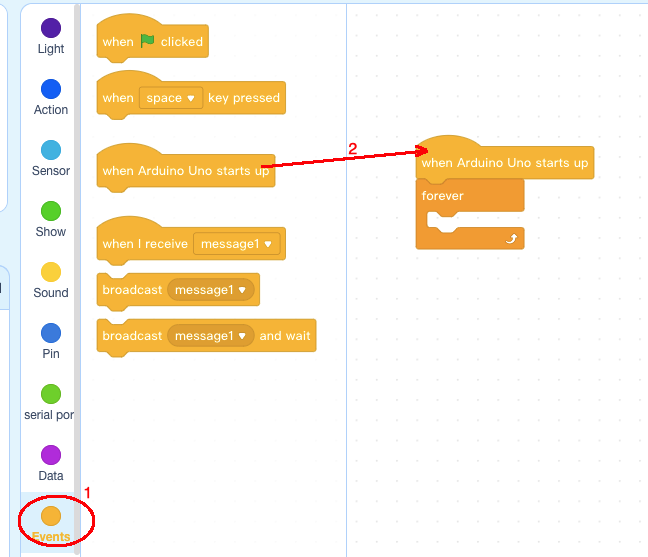
Step 2: Click Events, add when Arduino Uno starts up block to the top:
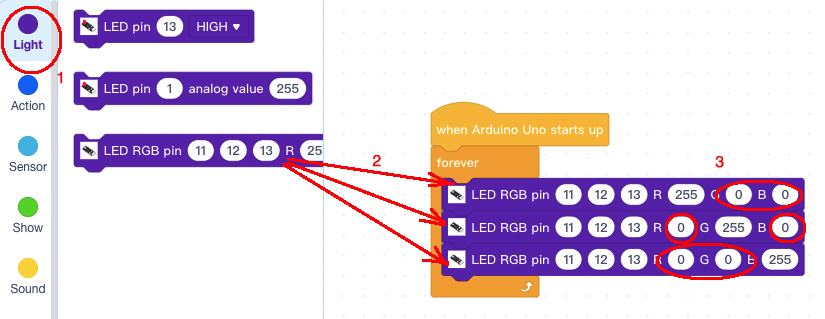
Step 3: Click Light, add 3 pcs of LED RGB Pin blocks inside forever block, then change some of the value from 255 to 0 as per following picture:
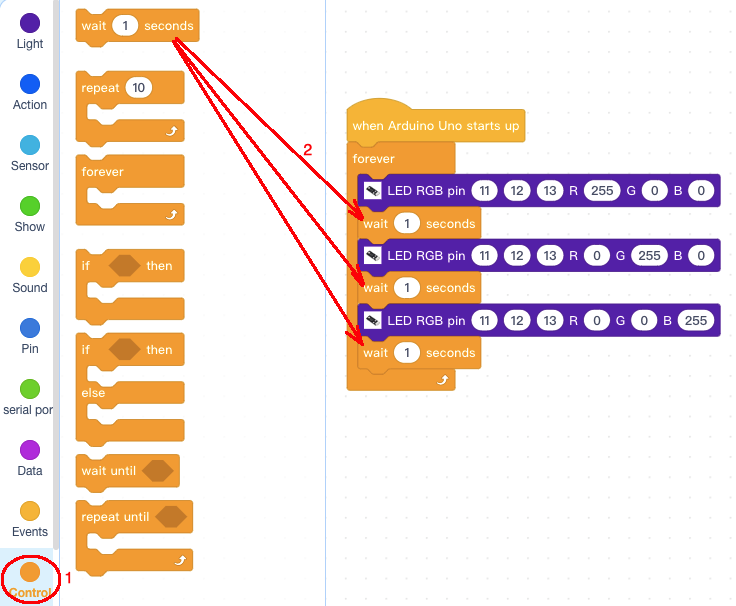
Step 4: Click Control, add 3 pcs wait 1 second block below each LED RGB pin block :
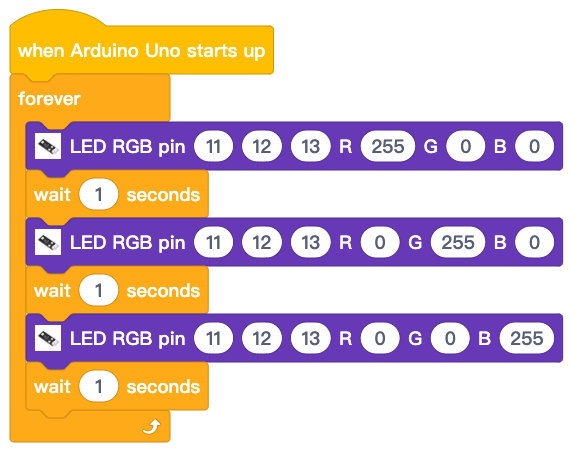
Now we have completed the block programming. The final blocks will look like following picture:
Upload the program to Arduino
1)you need click the Connect button in the bottom of the mBlock software, you will see a USB window pop up,
2) select Show all connectable device check box , then a device drop-down menu will show up,
3) select your Arduino port from device drop-down menu
4) click Connect button to connect your PC to Arduino
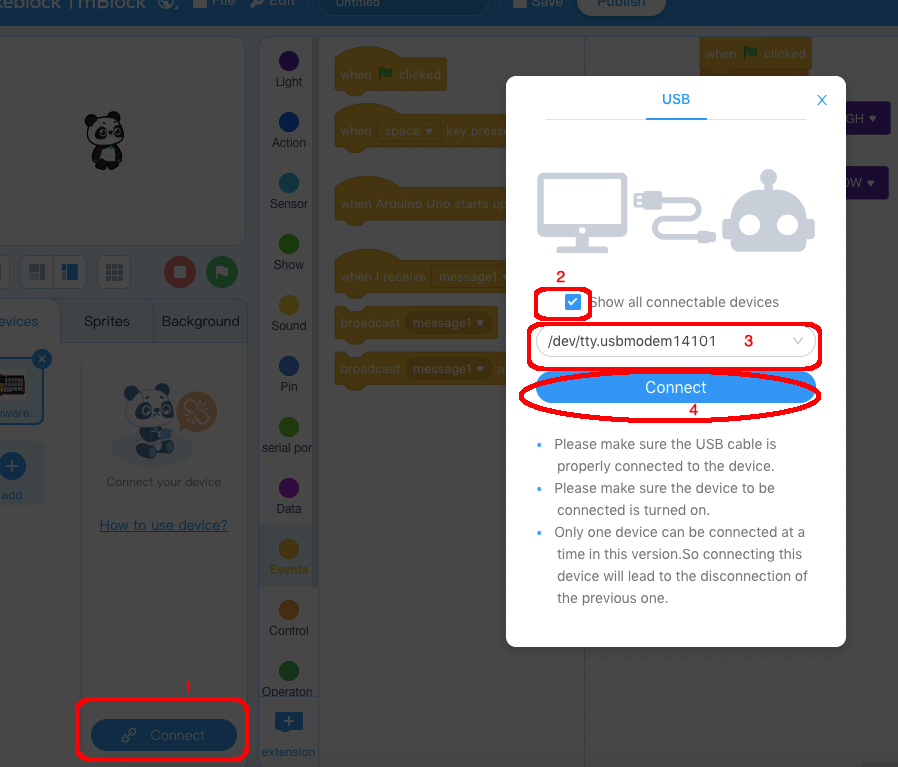
5)After you PC is connected to Arduino UNO board, please click Upload button in the bottom of your software, then the code will be uploaded to Arduino UNO board:
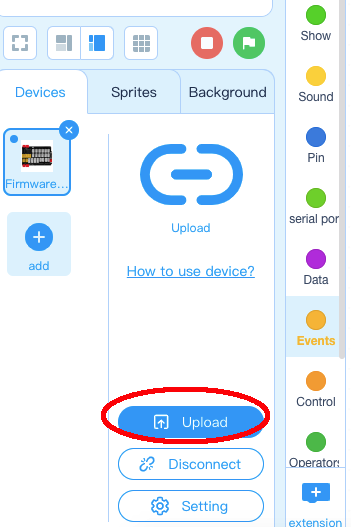
Test the program:
After you upload the code, the RGB LED module which rotate its color from Red to Green to Blue. Each color will pause for one second.