内容索引
- 什么是ARDUINO控制板?
- 为什么要使用ARDUINO控制板?
- Arduino控制板种类
- ARDUINO内部结构?
- 什么是Arduino IDE?
什么是ARDUINO控制板?
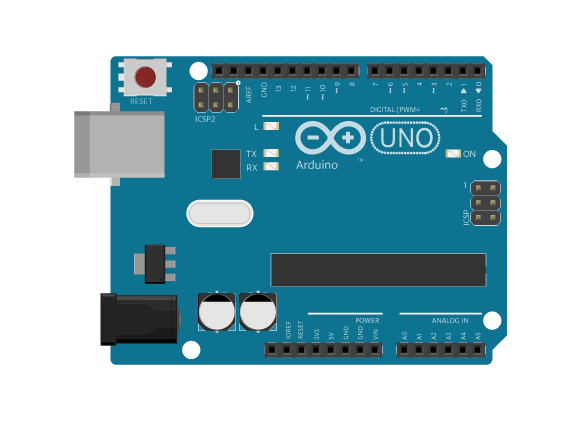
Arduino是由一家由意大利公司开发的微型计算机控制板(MCU)。它可以通过编程方式对各种电子器件和机械部件进行控制和通讯,完成各种创意产品的开发和设计,非常适合用于初学者学习计算机软硬件编程以及新产品开发。
Why choose Arduino?
相比其他MCU,ARDUINO控制器有如下特点:
- 软硬件全部开源,任何硬件厂家都可以自由生产而无需支付专利和版权费用。这样导致该款产品价格非常低廉,非常适合学生,业余爱好者等普通用户使用。又由于版权开源,导致大量自由程序员为它开发大量免费软件和创意作品,并在开源社区里面分享,使得初学者非常容易获得开发创意产品的灵感和解决方案。
- ARDUINO支持一个非常简单的集成开发环境(IDE),并把一些复杂的硬件编程方法封装到了一些函数库里面, 即使初学者没有太多计算机硬件知识也可以很快上手,并完成过去只有大公司资深工程师才能实现的创意产品。
- 与很多传统MCU不同,ARDUINO的软件烧录非常简单,只要一根USB电缆就可以把高级语言(C)代码转换为机器代码并一次性烧录到机器固件里面。
Arduino有些什么种类
Arduino 控制板有多种不同的类型,包括UNO, MEGA2560, Nano, Pro Mini(Pro Micro),Lilypad, Leonardo, Yun等。现在对最常用的几个类型分别介绍如下:
- 基本型ARDUINO UNO控制板 ,尺寸比一张银行卡略大一点点。有14个数字口,6个模拟端口,能完成大多数的ARDUINO基本功能。
- Arduino MEGA2560, 处理器更强大,端口更多,当然价格更昂贵,适合比较高端的应用。
- Arduino Nano,这是一种小尺寸的ARDUINO控制板,大概比UNO板小一半以上,适合于一些需要小尺寸控制板的场合
- Lilypad,这是一种微尺寸的控制板,大概只有一个硬币的大小,本身造型像一朵盛开的桃花,非常适合做时尚产品的控制器。
What Is Inside an Arduino / What’s on the board?
Don't feel like you have to understand this part fully! Skim it for now,
and consider it a resource for you when you want to take a deeper dive
into understanding the hardware!
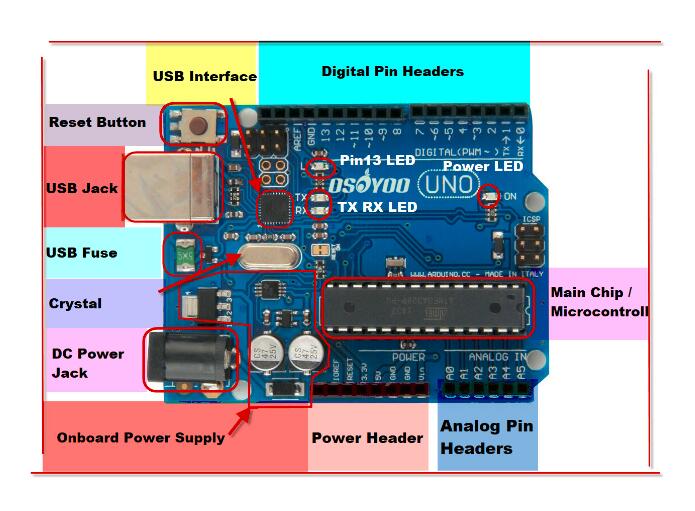
Main Chip / Microcontroller
The black thing with all the metal legs is an IC, or Integrated Circuit (13). Think of it as the brains of our Arduino. The main IC on the Arduino is slightly different from board type to board type, but is usually from the ATmega line of IC’s from the ATMEL company. This can be important, as you may need to know the IC type (along with your board type) before loading up a new program from the Arduino software. This information can usually be found in writing on the top side of the IC. If you want to know more about the difference between various IC’s, reading the datasheets is often a good idea.
<h3″>Power (USB / Barrel Jack)
Every Arduino board needs a way to be connected to a power source. The Arduino UNO can be powered from a USB cable coming from your computer or a wall power supply that is terminated in a barrel jack.
The USB connection is also how you will load code onto your Arduino board. More on how to program with Arduino can be found in our Installing and Programming Arduino tutorial.
NOTE: Do NOT use a power supply greater than 20 Volts as you will overpower (and thereby destroy) your Arduino. The recommended voltage for most Arduino models is between 6 and 12 Volts.
Onboard Power Supply
The Arduino is designed for beginners so it has some protection and regulation circuitry so that it can use just about any power supply you throw at it. In particular there is a polarity protection diode (to avoid destroying the board if you have a Negative Tip adapter). It also has an onboard 5V
USB Jack & Interface
USB Jack
As we talked about in the beginning, this is how you connect your Arduino to your computer. You can use any computer with a USB port. You will need a cable to connect! This cable is usually included in the Osoyoo pack.
USB Inteface Chip
OK so you plug your Arduino into a computer with a USB cable. But you may be surprised to learn, the main processor chip (ATmega328) cannot speak “USB”. Instead it can talk an interface language called “Serial”. Serial is a much simpler, much older interface. (It’s also a lot less expensive to build into a chip) So, how do you connect a chip that does not speak USB to a USB port? Easy! you just need a USB to Serial Interface Translator chip. Much like a human translator, it can understand and speak both languages and can seamlessly translate between the two.
There’s a lot of different translator chips, some common part numbers are FTDI FT232, FTDI FT231X, CP2102 orCP2104, PL2303, CH430 and probably a dozen others. They’re all nearly identical but some require different operating system drivers.
Arduino LEDs
Likewise, the Arduino has four LEDs: L, RX, TX, and ON
ON LED
This LED will shine green whenever the Arduino is powered. Always check this LED if your Arduino is not acting right, if its flickering or off then you should check your power supply.
RX and TX LEDs
These are like the ‘send’ and ‘receive’ LEDs on your cable modem. They blink whenever information is sent from or to the Arduino through the USB connection
The TX LED lights up yellow whenever data is sent from the Arduino to the computer USB port
The RX LED lights up yellow whenever data is sent to the Arduino from the computer USB port
L LED
This is the one LED that you can control. The ON, RX and TX LEDs all light up automatically no matter what. The L LED, however, is connected to the Arduino main chip and you can turn it on or off when you start writing code.
For future reference, L is connected to Digital Pin #13
Power Header
- Vin – This is connected to the power input from the DC Jack, so it is going to range from 7 V to 12 VDC, depending on what is plugged into the DC Jack. If the DC Jack is not powered, it will provide the 5V from the USB connection. Provides as much as the DC power supply can.
- GND – You get two of these here, they are the common ground connection for all power and data
- 5V – This is the clean regulated 5V power that the Arduino runs on, provided from the DC jack (if plugged in) or USB connection (if DC is not plugged in). Provides up to about 500mA current draw.
- 3.3V – This is a clean regulated 3.3V power, sometimes you’ll need exactly this voltage for some sensors. Provides up to about 100mA current draw.
- Reset – This is the same pin connected to the reset button
- IOref – Used by shields to know what the IO voltage is. You can ignore this pin.
- Unnamed pin – Reserved for future use, don’t connect to it!
Digital Pin Headers
The two pins labeled 0 (RX) and 1 (TX) are the two Serial pins that are used to send data to and from the Arduino to the USB-Serial translator chip.
Don’t connect anything to Digital 0 or 1 unless you are super sure because it will affect your Arduino’s ability to communicate!
- Digital 2 through Digital 12 are normal every day digital pins.
- PWM Pins: In the board, there is a ~ sign near to some of the pins – 3, 5, 6, 9, 10(digital pins) and 11 on the UNO Arduino. Actually these pins are normal digital pins but it can be used for Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) also.
- Digital 13 is a little special because it is also connected to the L LED. You can use this pin without affecting the Arduino just be aware that the L LED will also blink at the same time.
And a few extra straggler pins:
- A spare power GND Ground pin
- AREF – Analog Reference pin. Used for advanced analog sensor reading (You’ll learn about this later)
- Two unlabeled pins (the labels are on the bottom). These are the SDA and SCL pins, which are used for connecting I2C type sensors. They are connected inside the PCB to A5 and A4 We do not recommend usin these unless you have an I2C sensor
Analog Pin Headers
Shh! It’s a secret but those 6 analog input pins? They can also be used as digital input/output pins, they really are the most versatile pins!
Each analog pin can read a voltage between 0 and 5 V (the same voltage used to power the Arduino.
Once you get advanced analog skills you can connect the ARef pin to a different voltage like 3.3V and direct the Arduino to use Aref as the max voltage, then you can get more precision. But we’ll cover that some other day.
Do not connect a voltage higher than 5V to the analog input pins or you could damage them!
USB Fuse
The little USB fuse is a part that is used to protect your Arduino and computer. You’ll be connecting all sorts of wires to your Arduino and there’s a chance you will accidentally short out the power. To keep your electronics safe this resettable fuse will open up, much like the circuit breakers in your home.
Reset Button
Just like the original Nintendo, the Arduino has a reset button (10). Pushing it will temporarily connect the reset pin to ground and restart any code that is loaded on the Arduino. This can be very useful if your code doesn’t repeat, but you want to test it multiple times. Unlike the original Nintendo however, blowing on the Arduino doesn’t usually fix any problems.
Pins (5V, 3.3V, GND, Analog, Digital, PWM, AREF)
The pins on your Arduino are the places where you connect wires to construct a circuit (probably in conjuction with a breadboard and some wire. They usually have black plastic ‘headers’ that allow you to just plug a wire right into the board. The Arduino has several different kinds of pins, each of which is labeled on the board and used for different functions.
- GND (3): Short for ‘Ground’. There are several GND pins on the Arduino, any of which can be used to ground your circuit.
- 5V (4) & 3.3V (5): As you might guess, the 5V pin supplies 5 volts of power, and the 3.3V pin supplies 3.3 volts of power. Most of the simple components used with the Arduino run happily off of 5 or 3.3 volts.
- Analog (6): The area of pins under the ‘Analog In’ label (A0 through A5 on the UNO) are Analog In pins. These pins can read the signal from an analog sensor (like a temperature sensor) and convert it into a digital value that we can read.
- Digital (7): Across from the analog pins are the digital pins (0 through 13 on the UNO). These pins can be used for both digital input (like telling if a button is pushed) and digital output (like powering an LED).
- PWM (8): You may have noticed the tilde (~) next to some of the digital pins (3, 5, 6, 9, 10, and 11 on the UNO). These pins act as normal digital pins, but can also be used for something called Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM). We have a tutorial on PWM, but for now, think of these pins as being able to simulate analog output (like fading an LED in and out).
- AREF (9): Stands for Analog Reference. Most of the time you can leave this pin alone. It is sometimes used to set an external reference voltage (between 0 and 5 Volts) as the upper limit for the analog input pins.
What is the Arduino IDE?
Arduino provides an open-source and easy-to-use programming tool for writing code and uploading it to your board. It is often referred to as the Arduino IDE (Integrated Development Environment). The Arduino Software (IDE) is easy-to-use for beginners, yet flexible enough for advanced users.